Djibouti
Map Courtesy CIA World Factbook
The area of Djibouti has been occupied by several tribes, currently the Afar and the Somali Isa. These tribes had regular trade contacts with the Arabs, and adopted Islam as their religion. The Republic of Djibouti gained its independence on June 27, 1977. It is the successor to French Somaliland (later called the French Territory of the Afars and Issas), which was created in the first half of the 19th century as a result of French interest in the Horn of Africa. However, the history of Djibouti, recorded in poetry and songs of its nomadic peoples, goes back thousands of years to a time when Djiboutians traded hides and skins for the perfumes and spices of ancient Egypt, India, and China. Through close contacts with the Arabian peninsula for more than 1,000 years, the Somali and Afar tribes in this region became the first on the African continent to adopt Islam.
This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Djibouti". |
||||||||||
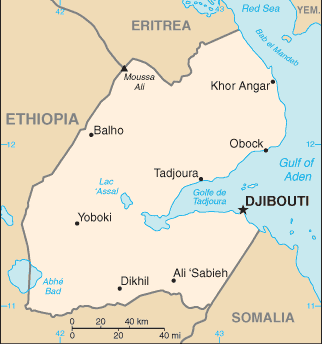 The Republic of Djibouti is a country in eastern Africa, located in the Horn of Africa. Djibouti is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Ethiopia in the west and south, and Somalia in the southeast. The remainder of the border is formed by the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. On the other side of the Red Sea, on the Arabian Peninsula, 20 km from the coast of Djibouti, is Yemen.
The Republic of Djibouti is a country in eastern Africa, located in the Horn of Africa. Djibouti is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Ethiopia in the west and south, and Somalia in the southeast. The remainder of the border is formed by the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. On the other side of the Red Sea, on the Arabian Peninsula, 20 km from the coast of Djibouti, is Yemen.