| Morocco
Map Courtesy CIA World Factbook
The full Arabic name of the country translates to The Western Kingdom. Al-Maghreb (meaning The West) is commonly used in Arabic. The name Morocco in most other languages originates from the name of the former capital, Marrakech (meaning "Country of God" in the Berber language). Morocco became a French protectorate by the signing of the Treaty of Fez on March 30, 1912. It remained a Kingdom until it achieved independence in 1956. It then recovered Tangier, formerly an international city. The northern area of Morocco was under a Spanish protectorate concurrently. Morocco annexed Western Sahara in the 1970s, which had been a colony under the Spaniards since the 19th century. Previous to that it had been an area of Moroccan influence, but this annexation has not been recognized by any nation. Morocco was the first nation to recognize the fledging United States in 1777 and has the oldest non-broken friendship treaty with the country, the Moroccan-American Treaty of Friendship, which has been in effect since 1783. John Adams and Thomas Jefferson were the American signatories. The United States legation (consulate) in Tangier, is the first property the U.S. owned abroad. It now houses the Tangier American Legation Museum. Morocco was granted Major Non-Nato Ally status in June 2004 and signed with the United States and the European Union free trade agreements.
|
|||||||||||||||
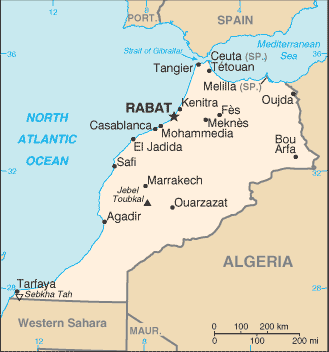 The Kingdom of Morocco is a country in northwest Africa. It has a long coastline on the Atlantic Ocean that reaches past the Strait of Gibraltar into the Mediterranean Sea. It borders Algeria to the east, though the Algerian border is closed, Western Sahara to the south and Mauritania, and the Atlantic Ocean to its north and west. Morocco claims ownership of Western Sahara and has administered most of the territory since 1975. The status of Western Sahara is disputed, pending a United Nations referendum.
The Kingdom of Morocco is a country in northwest Africa. It has a long coastline on the Atlantic Ocean that reaches past the Strait of Gibraltar into the Mediterranean Sea. It borders Algeria to the east, though the Algerian border is closed, Western Sahara to the south and Mauritania, and the Atlantic Ocean to its north and west. Morocco claims ownership of Western Sahara and has administered most of the territory since 1975. The status of Western Sahara is disputed, pending a United Nations referendum.