Seychelles
Map Courtesy CIA World Factbook
While Arab traders were probably the first to visit the uninhabited Seychelles, the first recorded sighting of them took place in 1505, by the Portuguese. As a transit point for trading between Africa and Asia, they were occasionally used by pirates until the French began to take control of the islands starting in 1756, naming them after Jean Moreau de Sechelles, the then French finance minister. The British contested control over the islands with the French between 1794 and 1811, with the British eventually gaining the upper hand and being ceded the islands in 1814. The Seychelles became a crown colony separate from Mauritius in 1903 and independence was granted in 1976, as a republic within the Commonwealth. The 1979 constitution declared a socialist one-party state, which lasted until 1992.
|
|||||||||||||||
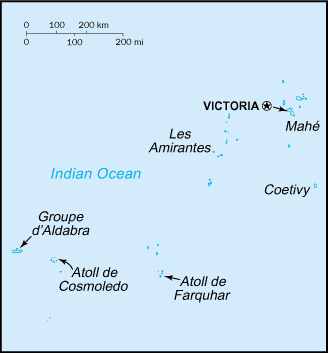 The Republic of Seychelles (say-SHELLS or say-SHELL) (Creole: Repiblik Sesel) is a nation of islands in the Indian Ocean, some 1,600 km east of mainland Africa, northeast of the island of Madagascar. Other nearby island countries and territories include Mauritius and Réunion to the south, Comoros to the southwest, and the Maldives to the northeast.
The Republic of Seychelles (say-SHELLS or say-SHELL) (Creole: Repiblik Sesel) is a nation of islands in the Indian Ocean, some 1,600 km east of mainland Africa, northeast of the island of Madagascar. Other nearby island countries and territories include Mauritius and Réunion to the south, Comoros to the southwest, and the Maldives to the northeast.