Guinea
Map Courtesy CIA World Factbook
In part of what is now Guinea, many empires rose and fell. Among them the Mandigo Mali Empire created by Soundiata Kéïta who defeated the Sosso ruler, Soumangourou Kéïta at the Kirina battle in 1235 which ended the Sosso Empire. The Mali Empire comprising parts of the northern part of Guinea was ruled by Mansa (Emperors). The most famous being Alhaj Kankou Moussa who made a famous pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324. The Mali Empire fell prey to the Almoravids invaders coming from north Africa who established the Songhai Empire which itself fell prey to the Maurs in 1591. Fulani Muslims migrated to Foutah Djallon in Central Guinea and established an Islamic state from 1735 to 1898 with a written Constitution and alternate rulers. Europeans adventurers started the overseas slave trade in the coastal region of Guinea from the 16th to the 19th Century. Present-day Guinea was created as a colony by France in 1890 with Noël Balley, being the first governor. The capital Conakry was founded on Tombo Island in 1890. Independent from France since 1958, Guinea did not hold democratic elections until 1993 when Gen. Lansana Conté (head of the military government) was elected president in disputed balloting. Security clampdowns continue, although not as severe as in earlier decades. Reelected in 1998, the President faced growing criticism in 1999 for his jailing of a major opposition leader and widespread economic malaise. Unrest in Sierra Leone also continued to threaten Guinea's stability.
|
||||||||||||||||
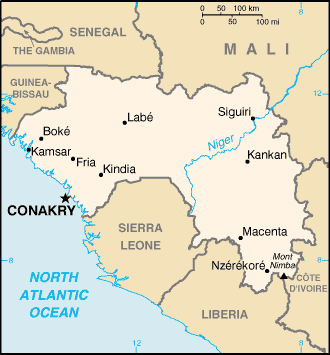 The Republic of Guinea (République de Guinée) is a nation in northwest Africa. It borders Guinea-Bissau and Senegal on the north, Mali on the north and north-east, the Ivory Coast on the south-east, Liberia on the south, and Sierra Leone on the west. Its territory encompases the water source for the Niger, Senegal, and Gambia rivers. The name Guinea (geographically assigned to most of Africa's west coast, south of the Sahara desert and north of the Gulf of Guinea) originates from Berber and roughly translates into 'land of the blacks.
The Republic of Guinea (République de Guinée) is a nation in northwest Africa. It borders Guinea-Bissau and Senegal on the north, Mali on the north and north-east, the Ivory Coast on the south-east, Liberia on the south, and Sierra Leone on the west. Its territory encompases the water source for the Niger, Senegal, and Gambia rivers. The name Guinea (geographically assigned to most of Africa's west coast, south of the Sahara desert and north of the Gulf of Guinea) originates from Berber and roughly translates into 'land of the blacks.